Why BPM Should Orchestrate and Agents Should Decide
By Satish Gupta • 1/18/2026
BPM for Control, Agentic AI for Intelligence
Most real GenAI automation use cases are landing in the Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) space. This involves tools like Kofax, Abbyy FlexiCapture for case initiation in the form of documents, calls received by a call centre agent, alerts triggered by monitoring systems, ECM for document storage, and a BPM layer for process orchestration.
Why BPM Still Matters
Every enterprise has a BPM layer for rule-based process orchestration, which is used for:
Clear end-to-end process orchestration
Clear auditability and traceability
Highly rule-based, predictable processing
An architecture pattern that can be used by a case management system can look like this:
BPM → LLM → Parse LLM Output → Define Next Step
But is this the right approach for GenAI automation?
The Role of LLM Orchestration Frameworks
Multiple LLM orchestration frameworks are available in the market, with LangChain being one of the most widely used. These frameworks provide the following flexibility:
Chains of sequences that can be dynamically defined by the LLM
LLM calls completely decoupled, making switching service providers plug-and-play
Context and memory management
Easy retry logic in case of failure
BPM can manage state very efficiently, and it can call LLMs. It can even retry calls. So should we not use LangChain or an LLM orchestration framework at all?
Decoupling BPM and LLMs
Here is my take on this:
BPM and LLM calls should be completely decoupled
BPM should orchestrate the process that is traceable, predictable, and accountable
BPM should call an AI service, and this is where a LangChain-like framework should be implemented
LangChain should take the input and process the document. Dynamic decisioning and probability-based statistics should be calculated here. This is where Agentic AI should come into the picture.
LangChain should send back:
Confidence score
Recommended next step
Reasoning / explanation
BPM should then decide the next step based on the confidence level. BPM should use a human-in-the-loop feature for accountability.
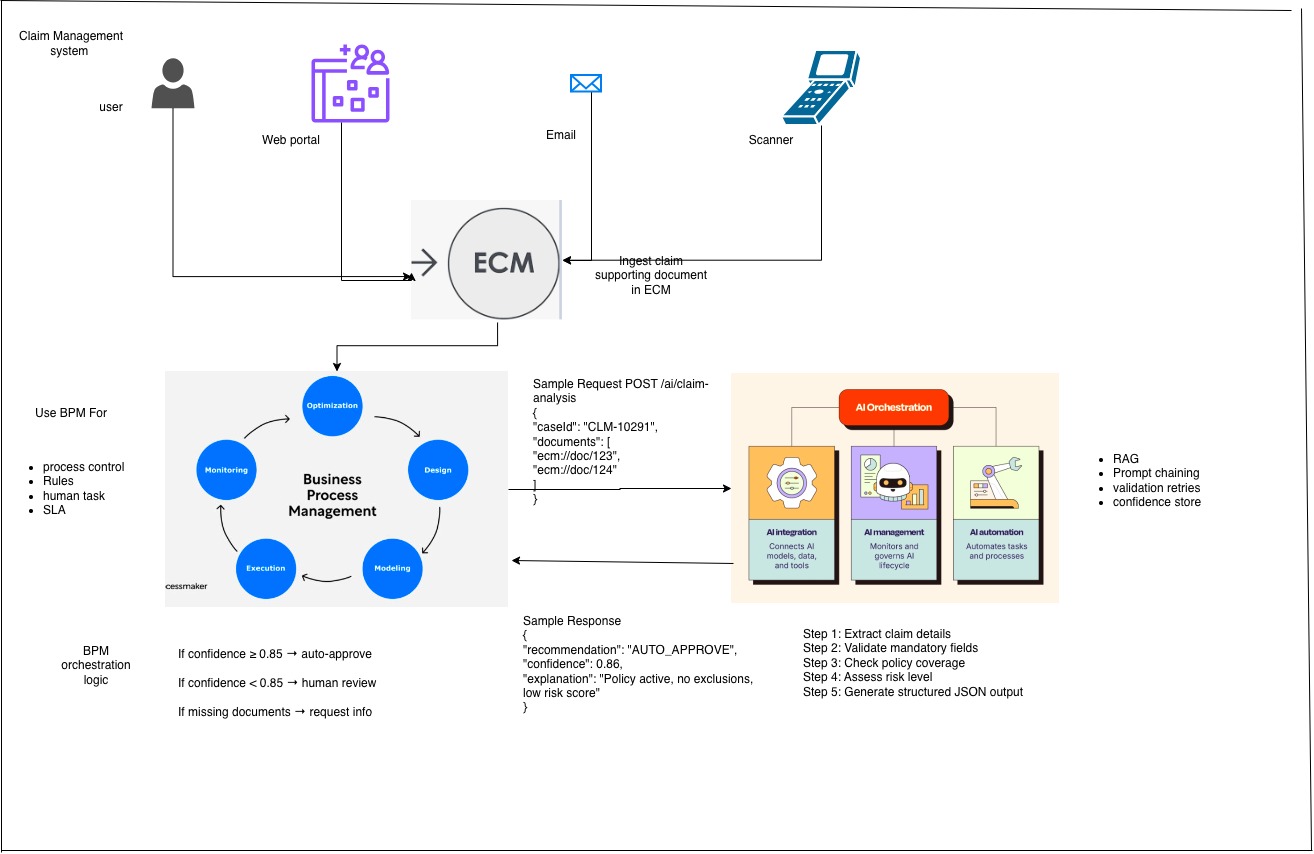
Claim Management Example Architecture
BPM: Case Initiation (Process Orchestration)
Handled by BPM (e.g., IBM BAW,Camunda ,JBPM)
A case is created when:
A claim is submitted via a portal
An email is ingested via ECM
Document is scanned via Kofax abby lex capture
BPM responsibilities:
Create case ID
Store metadata for supporting documen
Attach supporting documents in ECM
Key point: No AI logic here. BPM makes a REST call, not a direct LLM call. BPM remains deterministic. AI logic stays isolated.
LangChain: AI Orchestration (Core Intelligence)
Now LangChain takes over.
Document Loading and Chunking
LangChain:
Fetches PDFs from ECM
Splits text intelligently (claims, invoices, reports)
RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)
LangChain retrieves:
Policy documents
Claim rules
Past similar claims
This context is injected into the prompts.
Agentic Workflow:
Extract claim details
Validate mandatory fields
Check policy coverage
Assess risk level
Generate structured JSON output
Output Validation and Retry
LangChain:
Enforces JSON schema
Retries if output is invalid
Falls back to another model if required
Example output:
{ "claimAmount": 12000, "coverage": "YES", "riskScore": 0.32, "confidence": 0.86, "missingDocuments": [] }
LangChain → BPM Response
LangChain returns decision support, not the final decision.
{ "recommendation": "AUTO_APPROVE", "confidence": 0.86, "explanation": "Policy active, no exclusions, low risk score" }
Rule-Based Decisioning in BPM
Now BPM does what it does best.
Example BPM rules:
If confidence ≥ 0.85 → auto-approve
If confidence < 0.85 → human review
If documents are missing → request information
No probabilistic logic inside BPM.
BPM: Human-in-the-Loop Review
If routed to a human:
Reviewer sees:
AI recommendation
Confidence score
Explanation
Reviewer actions:
Accept
Override
Request more documents
All actions are:
Logged Audited SLA tracked
Finally:
Update claim status
Notify customer
Archive documents in ECM
Close case