Inference in Large Language Models
By Satish Gupta • 11/30/2025
In this article, I want to discuss the concept of inference in large language models. With the rise of cloud-based inference services from providers like OpenAI, Microsoft, Google, and Groq—each generating significant revenue—many people rarely talk about what inference actually is.
Understanding inference is essential before starting any Generative AI project because it fundamentally changes how we view large language models (LLMs). LLMs operate purely on mathematical principles. However, since most developers rely on cloud inference, this core concept is often ignored. Many solutions I see today use frameworks like LangChain or n8n with cloud inference, making projects look complex on paper but often fail in practice. Could the lack of basic understanding be the reason? In my experience, yes.
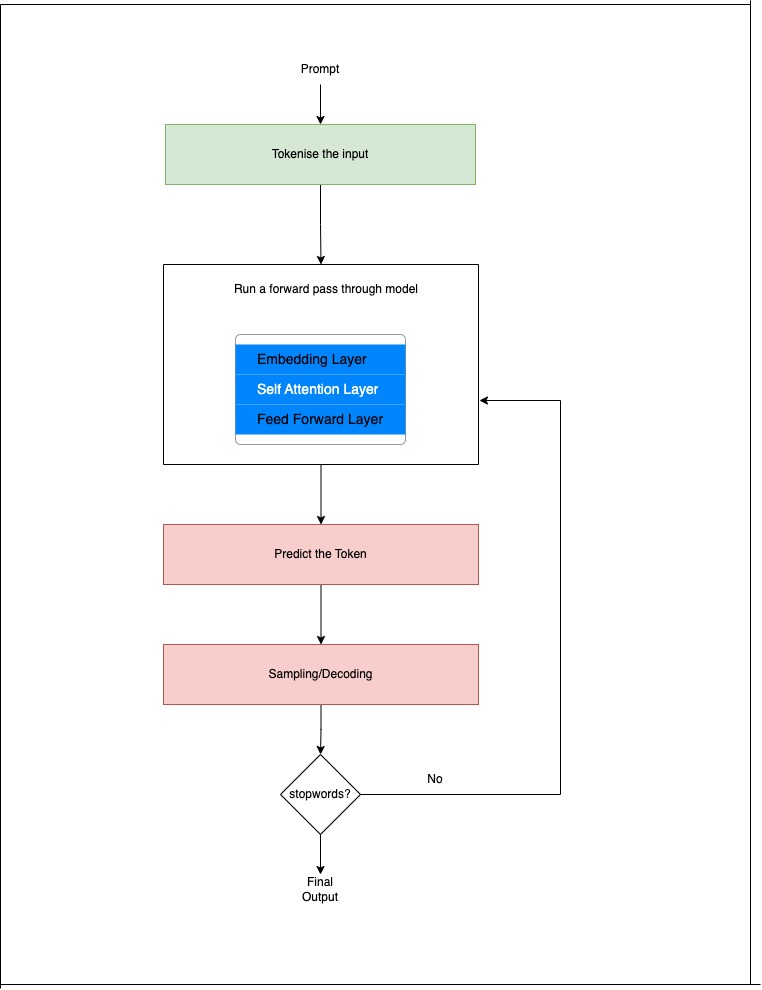
In this article, I explain inference in a simple and practical way using a five-step process: The Five Steps of LLM Inference
1. Tokenize the Input
The prompt is converted into tokens. Tokens are numerical IDs that correspond to entries in the model’s vocabulary.
2. Run a Forward Pass Through the Model
The tokens are fed into the transformer model, where they pass through:
Embedding layer
Self-attention layers
Feed-forward layers
Each layer refines the token representations. This internal processing is complex, and I may explain it further in other articles in a simpler way.
3. Predict the Next Token
The model outputs a probability distribution over the entire vocabulary.
Example:
If Hello is given as prompt , model will output probability distribution like below .
"!" → 0.42 "world" → 0.15 "." → 0.10
4. Sampling / Decoding
Based on the decoding method (e.g., top-k, temperature), the next token is selected.
5. Repeat
The newly generated token is fed back into the model, which predicts the next one, and this loop continues until the model stops.